Crypto Bonds
Welcome, premium subscribers! Thank you for subscribing. What will be shared today and the days ahead are alpha from our Economics Design's researchers. Please keep these mails secret and do not share them with any one because these alpha are confidential. Enjoy your reading.
TLDR below. This is not financial advice.
General Conclusion
Bonds are one of the most in-demand financial products to date. According to Icmagroup, the total bond market is over $128Tn and the terrain is open for blockchain projects to penetrate the market.
Many new DeFi projects are looking at concepts found in traditional finance, such as:
-
Fixed interest;
-
Decomposing fixed income assets into principal and interest;
-
Leveraged yield.
DeFi protocols are beginning to address basic concepts and meet the needs of many classes of users that TradFi cannot, because of crypto’s nearly frictionless composability.
These protocols were born with the primary goal of uncertain and often volatile returns received when staking or depositing tokens for lending (Aave, Compound), trading (Curve) or actively farming (Yearn, Harvest).
Traditional Bond
Definition
A bond is a security issued in connection with a debt arrangement. The borrower (the seller) issues a bond to the lender (the purchaser) in return for some cash. A bond is an “IOU” (I Owe You) of the borrower. A typical coupon bond requires the issuer to make predetermined payments.
When the bond matures, the issuer repays the debt by paying the face value of the bond. The bond’s interest rate determines the interest payment. The annual payment amount equals the bond’s interest rate multiplied by the bond’s face value. The coupon rate, maturity date and par value of the bond are part of the bond indenture agreement, which is a contract between the issuer and the holder of the bond.
Types of Bonds
-
Government bonds
This is a type of security issued by a government for the purpose of raising medium and long-term capital for the government. Revenues from bonds can be used to make up temporary shortfalls of the state budget, to implement national construction projects, or to finance other government purposes according to the budget allocation plan. books every year.
-
Local Government bonds
These are bonds issued by the People’s Committees of provinces and centrally run cities to raise capital for local investment projects and works.
-
Government-guaranteed bonds
This is a bond issued by enterprises, financial institutions, credit institutions, and policy banks of the State subject to the provisions of the relevant laws and guaranteed for payment by the Government.
-
Corporate bonds.
Debt securities are bonds issued by companies or financial institutions in order to raise capital for business activities.
Pricing
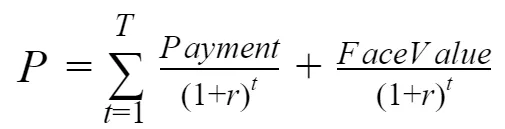
In which:
T is the time to maturity
r is the discount rate
Note: The discount rate is determined before the bond is sold and remains constant throughout the life of the bond T.
Decentralised Bond
Definition
By definition, it is clear that decentralised bond has the same meaning as traditional bond. Some of the differences include the time to maturity, the yield, and the ability to combine to create many different products and serve different purposes.
Type of Bonds
Most projects offer two products at the same time to take full advantage of blockchain and as a mechanism to transfer risk between two groups of people: (1) those wanting a fixed interest rate and (2) those wanting to speculate based on fluctuations in interest rates.
Barnbridge SMART Yield, 88mph, Pendle, APWine, Element and Swivel are focused on this decomposing:
-
A Fixed Rate Asset (or Zero-Coupon Bond);
-
Floating Rate Bond (or a “floating” yield token, or tranche).
Other protocols such as Horizon and SwapRate also involve fixed and floating decompositions, each in their unique way.
Case Studies
BarnBridge
BarnBridge (BOND) is a derivatives protocol (cross-chain enabled) that allows tokenising of “risk” into bonds with relatively stable interest rates.
What is SMART Yield?
SMART Yield allows users to export their interest rates from lending pools on platforms like Aave, Compound, Cream, Yearn Finance to normalise the risk curve by creating derivative assets to convert risk .
BarnBridge has introduced the SMART Yield operating system that has two main components:
-
$jTokens for lenders that accept fluctuations in interest rates.
-
$sBONDs for lenders who need a fixed interest rate.
-
-
DeFi Risk Management Tool – Tranche Junior and Senior
Tranches in the traditional market are mortgage-backed financial assets, which form a pool of mortgage loans pooled by centralised institutions so that investors can invest easily, and creating liquidity high account.
BarnBridge’s Tranche Junior is riskier and has a highly volatile APY in line with market averages, while Tranche Senior has lower volatility with near-variable interest rates.
-
How BarnBridge Works
The liquidity provided by Junior and Senior tranche investors on the BarnBridge platform will be distributed evenly across different lending platforms (Aave, Compound, Cream …), and then a fixed portion of it. The fixed rate of interest will be used to pay Tranche Senior investors.
The liquidity reward paid in the governance token of that lending platform will be automatically sold by BarnBridge on Uniswap to investors.
Example:
-
Compound is the lending platform used, $USDC is the pool provided with liquidity. In the event that Compound’s APY is higher than the promised APY to be paid to $sBONDs holders, $jTokens holders will receive a larger-than-usual reward.
Conversely, in the event that Compound’s APY is lower than the APY promised to pay $sBONDs holders , $jTokens holders will receive a lower reward than usual, as that interest is deducted to pay $sBONDs holders.
-
Advantages for Tranche Junior Users
Tranche Junior has a lot of risk so it is possible that the number of users will not be proportional to that of Tranche Senior.
Therefore, to encourage users of this tranche, BarnBridge allows them to participate in tranches at any time, instead of just depositing and withdrawing based on maturity like the Senior Tranche. To do so, the team has to calculate the pool’s profits and risks very carefully.
Furthermore, Tranche Junior users are able to withdraw part of their funds from the pool at any time without affecting other users. $jTokens is an ERC-20 token so it can also be traded in the secondary markets. Finally, $jTokens holders can participate in BarnBridge DAO’s liquidity mining programme to earn extra profits.
In short, Tranche Junior investors bear the risk for Tranche Senior investors. In the case of SMART Yield, the risk of Tranche Junior investors is the risk that the average APY of the lending pools (Aave, Compound, Cream …) will decrease. Senior tranche investors will own $sBONDs and receive a constant interest rate for the duration of their ownership of the token.
Swivel Finance
Swivel Finance is fixed-rate lending and interest-rate derivatives.
The project allows the party that needs a fixed interest rate (Fixed Side) to match orders directly with the party that wants a floating interest rate (Floating Side) for a specified period of time through a marketplace provided by Swivel Finance.
-
How Swivel Finance Works
Swivel Finance allows users to match orders and the total amount matched can be transferred to a smart contract.
The smart contract then transfers funds to Aave or Compound for lending, receiving $aToken/$cToken and locking them up to the agreed time.

Source: Swivel Finance
Example:
Alice has $1,000 to lend at a fixed rate of 5% APY, Bob thinks that in the next 12 months the floating rate on Aave will be more than 10%. Bob goes to Swivel Exchange and sees Alice placing an order of $1,000 with 5% fixed rate, so Bob buys it.
At this point, Bob only needs to provide $50 for execution because the rate is fixed at 5%. After $1,050 is transferred to the Swivel Finance contract, it will be transferred to Aave floating rate lending.
A year later, the contract expires, the interest is now 12%. Bob gains 152% when he only needed to put in $50 and receives $126. Alice gets $1,050 as in the original deal.
-
100x higher trading leverage
Swivel claims to be able to offer trading leverage of 10 to 100 – much higher than 0.5 to 0.75 from other platforms such as Yield, Notional, UMA, and Mainframe by removing excess collateral levels.
They are confident that, with such superior leverage, they can get ample liquidity from interest rate speculators.
In order to avoid confusing investors, Swivel reaffirms that they only provide high leveraged interest rate speculation and fixed rate lending services, not lending services (borrowing) with a fixed interest rate. You should distinguish clearly to avoid causing confusion, leading to unnecessary property loss.
-
Advantages
Fixed-Side/Floating-Side Rate-Swap Contract: Swivel Finance provides users with two options:
-
With Fixed-Side, users can place their order above the market rate, which is similar to a limit order.
-
With Floating-Side, users can place their order below the market rate, which is similar to a market order.
Swivel Finance off-chain/on-chain orderbook: Swivel Finance’s order book will provide two versions for users to choose from: on-chain and off-chain.
-
TLDR:
Recently, the cryptocurrency market has become more and more exciting because of the rapid increase in the number of new participants. In the current situation of extremely low bank interest rates, more and more people with a demand for “fixed interest rate loans of 10% a year” will step into this market.
Applications like Outlet, Linus, Dharma, BlockFi, Celsius have developed user interfaces to meet this need, with liquidity coming from centralised liquidity pools or from Compound and Aave. Therefore, users’ attention to decentralised fixed-rate products will be even greater.
