The Layers Of Blockchain
This is not financial advice.
Catch the episode on YouTube

Introduction
DeFi is still a little bit complicated and we want to explain the entire technological stack so that it gives you a snapshot of everything. What we’re trying to do with decentralized technologies is to build a whole new infrastructure of financial layers which will coexist together with the traditional finance or the capital market that we have today.
Layers of Blockchain
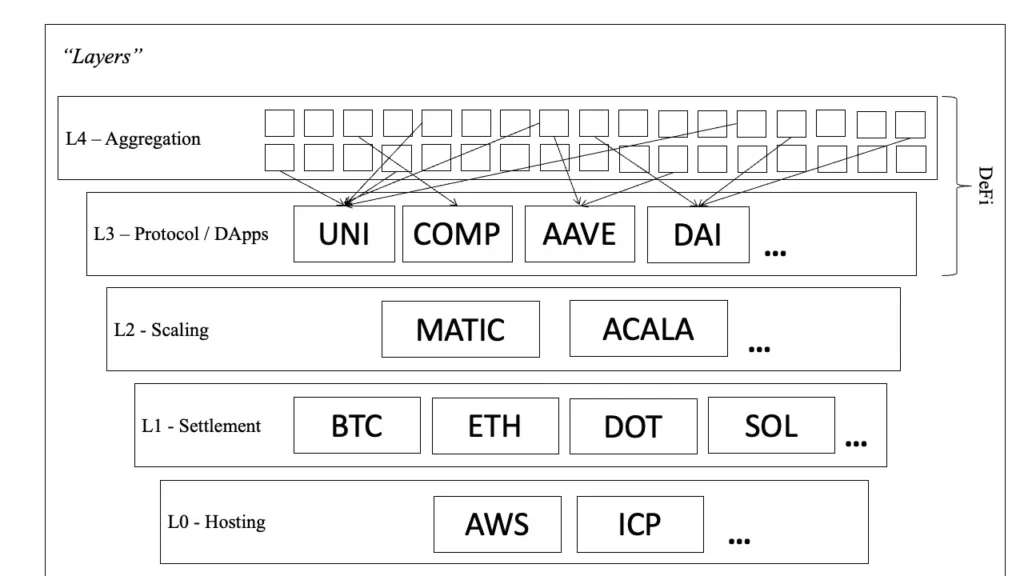
Base/Hosting Layer
The hosting layer is where you host all these different transactions that take place. For example, this could be stuff like AWS (Amazon Web Service) or this new thing that they’re building out called the Internet Computer Protocol.
Settlement Layer
We are hosting all these transactions but who will account for them or settle them? This is where the settlement layer comes in and in this layer, we have Bitcoin, Ethereum, Polkadot, etc. This is where all the transactions that are going on need to be accounted for. You can think of it as a big accounting book for everything that’s going on in the network.
Scaling Layer
You don’t really need this and it’s just a way for you to create more transactions. Here you have projects like MATIC or Arbitrum, which are built on top of the settlement layer but are much faster and cheaper. This allows you to transact a lot better. At the end of the day, all the settlements will go back to the bottom layers but the scaling layer will help you to execute more things faster and at a cheaper rate.
Application Layer
This layer is where you have specific things being built. For example, with UNI, it is for you to trade. It’s like the decentralized NASDAQ. COMP and AAVE are basically decentralized banks that facilitate lending and borrowing. Then you have DAI which is your decentralized USD. These are very specific kinds of applications that are not run by a centralized authority. They’re protocols or machines that execute these applications and that’s why it’s a protocol layer or the application layer.
Aggregation Layer
The aggregation layer is where they take in all the different kinds of information and aggregate things together. It is similar to apps like google news that aggregate different information from different news sources into a single app.
What Is DeFi?
The application/protocol layer as well as the aggregation layer is where you have a lot of decentralized finance applications. All the bottom layers are the basic infrastructures which are important in different ways. They’re more of the supporting infrastructure. Usually, when we’re talking about decentralized finance, we are referring more to the aggregation layer and the protocol or application layer.
Conclusion
To better understand the difference between Crypto and DeFi, we took a look at the different layers. Each layer has its own feature. In DeFi, we are usually referring to the Application/Protocol layer or the Aggregation layer.
