This is not financial advice.
In early 2021, we had discussions on the idea of building a decentralised Internet, commonly referred to as Web 3.0.
-
In the United States President Trump has been banned from using Twitter, and Parler, which uses AWS services, has been removed from PlayStore and AppStore.
-
WhatsApp has announced that they will share information with their parent company Facebook
-
Uganda has ordered internet service providers to block all social networking platforms
These are important and understandable issues and need to be actively discussed.
Small businesses and startups rely on Facebook advertising services, Google search suggestions, and Amazon’s AWS service to survive. Artists and creators face the risk of having their information deleted from sites like Spotify, Instagram and Tiktok. Although these are not new problems, it is becoming more and more serious. The development of technology monopolies and their scalability to information privacy rights and personal freedoms has spurred the Internet transition from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0.
What Is Web 3.0?
In short: Web 3.0 is the next era of Internet.

Image credit: blockgeeks.com
Web 3.0 (commonly called Web3) is a reform model aimed at democratising the Internet. Web 3.0 is present in the Crypto Space and other digital fields such as AI, Virtual and Augmented Reality, and more. By applying new technologies, Web 3.0 is changing how we, as a collective, view and value the Internet. Web 3.0 is about creating an Internet that works for everyone, owned by everyone.
Where Web 3.0 Comes From
The term was originally coined in 2014 and popularised in 2018 by Ethereum co-founder and Polkadot founder Gavin Wood. The spirit of this term goes back to when Satoshi developed Bitcoin and advocated decentralised DNS called BitDNS.
“I think it would be possible for BitDNS to be a completely separate network and separate blockchain, yet share CPU power with Bitcoin.” – Satoshi (2010)
DNS has long been controlled by organisations such as Verisign and the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) overseen by the US Department of Commerce. This centralised control of DNS has been used to enforce IP rights, prohibit websites from selling copyrighted material, censor free-of-speech sites like WikiLeaks and seize domain names (IP addresses) without proper procedures, etc. Censorship decisions are usually influenced by the top levels of government and the lobbyists of the largest multinational organisations, who may not always be acting in the best interests of the general public.
Satoshi and other Bitcoin enthusiasts recognised this. In 2011, a fork of Bitcoin called Namecoin was born to allow censorship-proof domains at .bit domain addresses.
Namecoin was ahead of its time. A proxy service or extension (such as MetaMask today) was required to log in at the .bit domain, making it very difficult to use. Plus, most people did not want their own website or personal domain at that time. All of this caused Namecoin to fail because of low demand from its users.
Ten years later and now new blockchains and decentralised services may be ready for success. These applications are making the Internet more decentralised with Web 3.0. Another example of such infrastructure is the Handshake network.
The Internet
The Internet has changed almost everything. This is emphasised because it has profound effects on economic, political or social issues.
Zero To Hero
-
Economical: The Internet has contributed to the development of globalisation and e-commerce. In particular, e-commerce has been outstanding in the COVID-19 era (the catalyst for this sector). Also in the past three years from 2017 to 2019, the S&P 500 technology sector index has doubled in value, and today e-commerce makes up about 25% of the S&P 500 index basket.
-
Social: Young companies in the past like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter and Google have spent a lot of money (40% of venture capital) promoting new startups. In addition, TikTok is also a growing and promising social networking platform for influencers on social networks.
-
Political: The media all use the Internet as a primary tool to spread political content, incite or defuse related issues. The Internet has influenced the world’s political elections and spawned a new generation of leaders who prefer to use the Internet as a new and effective tool.
The Internet has changed almost everything from financial markets to culture and elections. For the foreseeable future, events originating directly from the Internet will shape the world many times over. And make the Internet more important than ever.
Today’s Problems
Although the Internet contributes a lot to people’s lives, it is largely controlled by organisations and governments. Global problems — like internet centralisation — are not the only factor.
Poor Ability To Create Value
Value from an internet service is less likely to be profitable.
iMessage is a very valuable service that is provided freely by Apple because there is no way to effectively monetise such a service. Almost every social network offers a free and unlimited message service between users. This is also a mandatory service and users will not want to pay for it.
The “giants” can monetise the above services through having byproducts like advertising or buying a project that is growing well in terms of users in the way that Facebook bought WhatsApp. This is not because of WhatsApp’s underlying technology, but for the long-term gain of acquiring users and their data.
Monopoly Infrastructure
Developers whose messaging service is the core product to engage users need free or low-cost infrastructure. Services are monopolised by Google and Facebook ads, allowing those companies to pay tens to hundreds of millions of dollars in expenses for whatever they need.
This has resulted in a natural monopoly on the data and distribution layers of the internet.
-
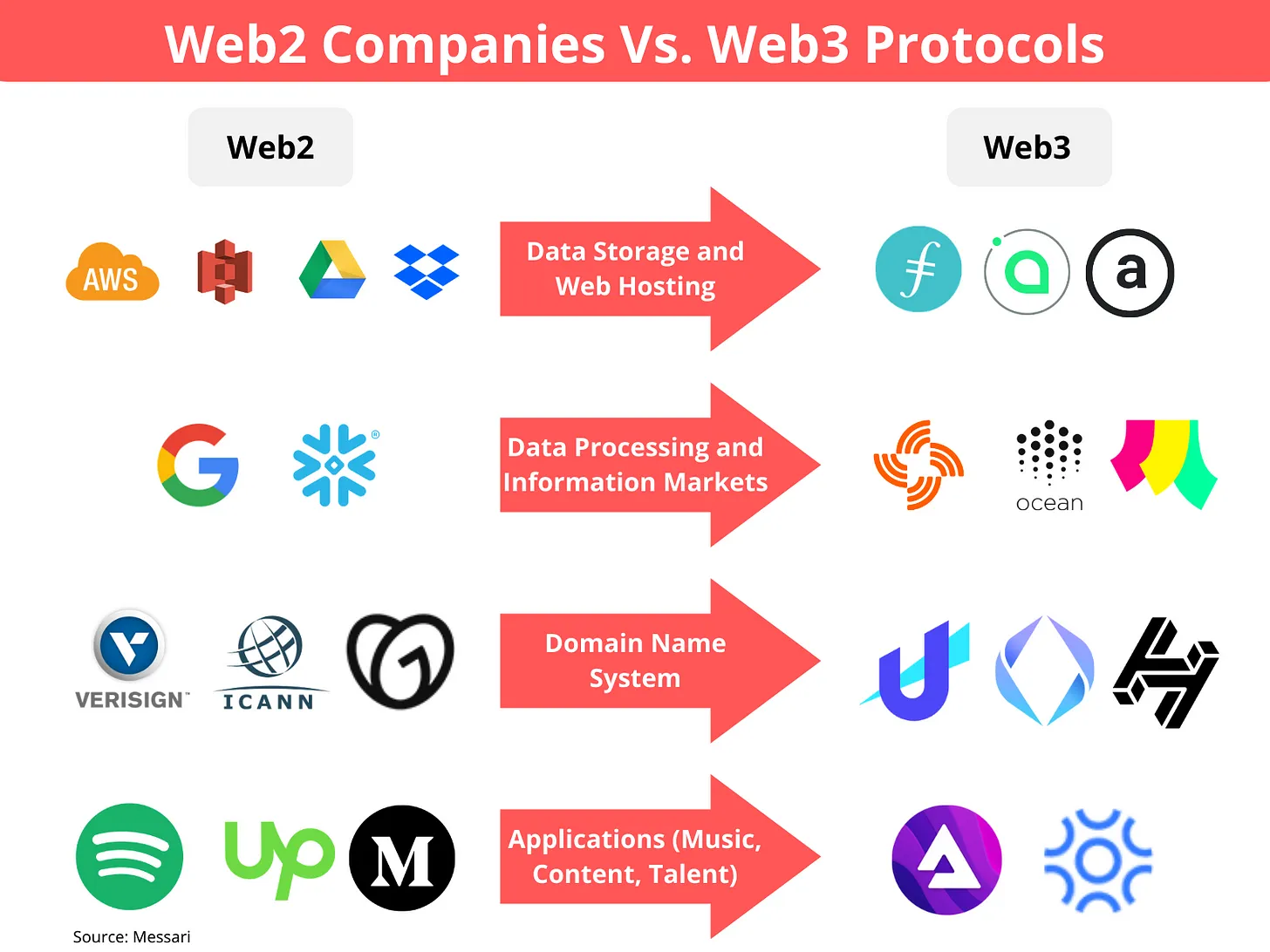
Data centres that provide cheap and fast access to computer and data storage are mostly controlled by providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google, Microsoft, and Alibaba.
-
Most open-source companies and projects rely on Github to host their code and manage software development.
-
The distribution of mobile applications is limited by phone manufacturers in the form of Google and Apple App stores.
In the past, these services were options for infrastructure. Today, these services are often bound by the terms of a company’s size or degree of success — from “options” to “monopoly”.
Outdated And Misled Regulation
Regulation certainly offers a potential solution for a wide range of infrastructure and internet services. Unfortunately, large companies and organisations often lobby lawmakers to prevent any significant change in the interests of consumers. Progress has been made now, but still very little.
Centralised Information And Data
Data is of no value if we do not know how to classify and label it. Large companies typically collect data, process it, create a more compelling data set and eventually use it for other applications and services, thereby attracting more user data.
Why Web 3.0 Is Important
The Internet’s early years were experimental and exploratory. Technology pioneers exploited, isolated and made information available on the Internet. To this day, the Internet is still free but with lots of bugs.
Our transactional information is recorded, sold or worse, used against ourselves. You can use the Internet but it’s not yours. Thus, there is an incentive to improve the existing system.
As an example of what is going on in today’s social network, I just talked about a dog across the street. Immediately on my account appeared a series of ads related to pets. Really annoying and I know that they are recording me through electronic devices.
A prominent feature of the Internet is the right to information and to democratise it. However, the information today is increasingly unreliable, unclear, or harmful. Fake accounts are created by bots to manipulate information. AI can draw faces and create huge problems for society through tampering and identity theft. Fake news has caused more than $70B of damage in 2019. People share and spread untrue information or fake news which moves x6 faster than real information because of the recoil tendon of information, which can be considered as digital viruses from humans.
A Shared World: Open-Source Protocol
Web 3.0 is rearranging existing Internet products and services so that they are of greater benefit to the community rather than companies/governments/entities. A vision of Web 3.0 Space is a world with open-source protocols, while businesses provide an interface for more convenient user access, plus additional features. Web 3.0 is an Open Internet for all users, built on open-source protocols and a transparent Blockchain network. Users communicate with protocols made possible through incorporated applications (such as Metamask) which interact with them.

DeFi Is A Necessary Infrastructure For Web 3.0
The first infrastructure necessary to achieve Web 3.0 is to create Internet native money. Bitcoin and Ethereum have emerged as the Internet money of the future, and it’s no surprise that this is where the first wave of innovation and testing is unfolding. The larger theme of Decentralised Finance (DeFi) is urgent for the development of Web 3.0.
Typical financial products from blockchain and DeFi such as AMM, Liquidity Mining, Stablecoin and Governance will be necessary to increase the coordination between Web 3.0 platforms.
Once Web 3.0’s financial system is stabilised, new business models and innovations will help reshape existing Internet products and services.
Conclude
The early internet needed avant-garde programmers and businesses to develop new products to make the Internet useful and to be rewarded for the value they created. No one knows in advance what the consequences of their construction will be.
Cryptonetworks, with their open source protocols and everyone-owned networks, offers the opportunity to restructure the Internet into a system that benefits more people around the world. This is a vision worth striving for.
The world evolving today is increasingly controlled by technology, so we must design systems that benefit the collective. The transformation of the Internet, from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0, is diverse and will change the way we interact with the Internet.
Ps: Order the textbook “Economics and Math of Token Engineering and DeFi” today!
